A Users Guide To Immortality
Aging In Humans Reversed With Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Aging, which happens over time in humans, has been biologically reversed by hyperbaric oxygen therapy, according to new research published in the journal Aging. Aging In Humans Reversed With Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
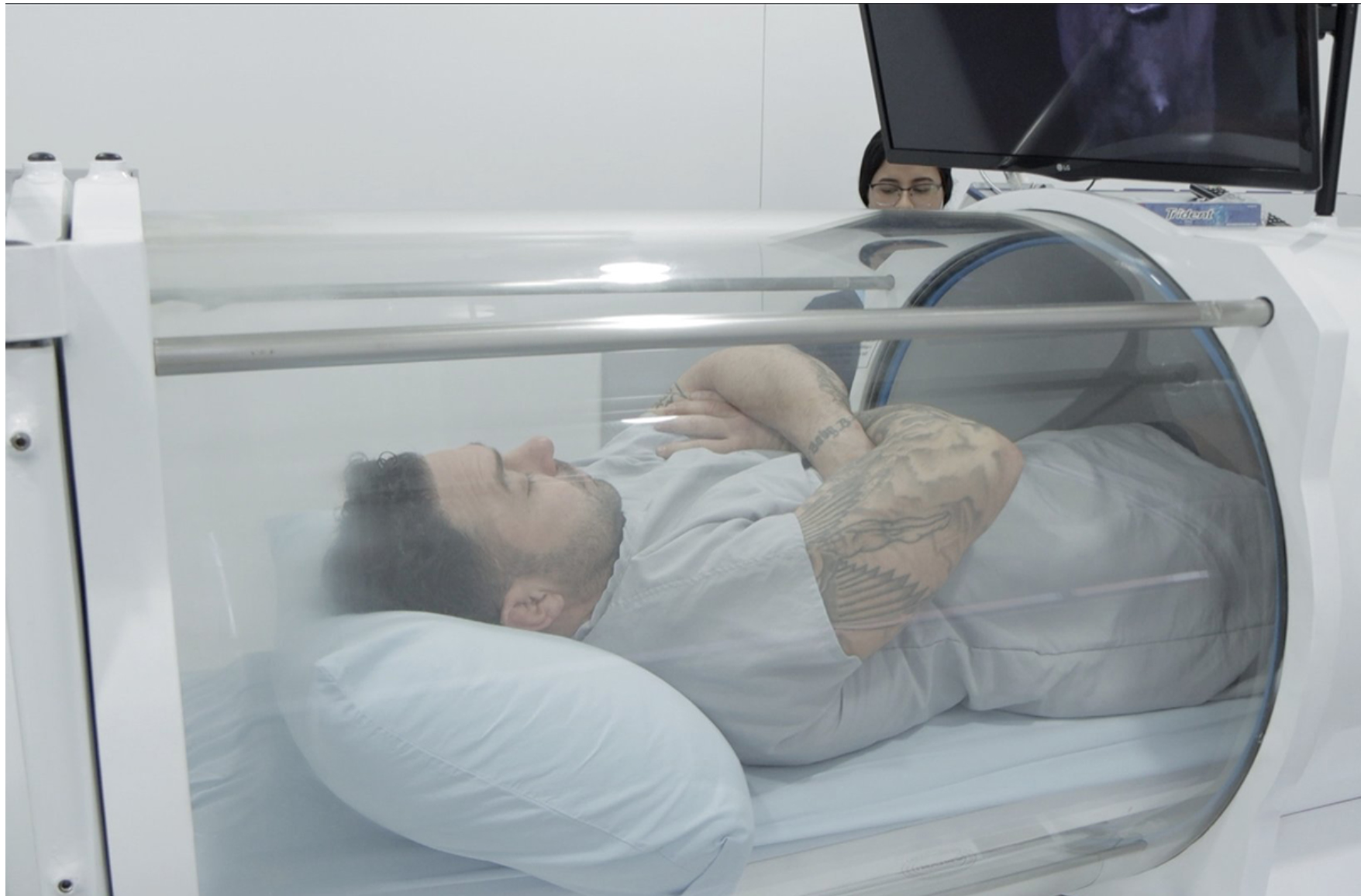
Scientists, led by Yafit Hachmo, from the Research and Development Unit, Shamir Medical Center, Tzrifin, Israel, turned back the human clock for 35 adults aged 64 and older by reversing two key areas of the body thought responsible for the frailty and ill-health that comes with growing older.
Protective caps at the ends of chromosomes, known as telomeres, shorten, causing DNA to become damaged and cells to stop replicating as people age. At the same time, senescent cells build up in the body, preventing regeneration.
Related:
Bitcoin Community Leaders Join Longevity Movement
Increasing telomere length and getting rid of senescent cells is the focus of anti-ageing research, with drugs being developed to target those areas, The Telegraph reported.
The 35 patients were repeatedly given pure oxygen in a hyperbaric chamber, which increased the length of their telomeres by 20%, a feat that has never been achieved before.
Scientists said the growth may mean that the telomeres of trial participants were now as long as they had been 25 years earlier.
The therapy also reduced senescent cells by up to 37%, enabling new healthy cells to regrow. Animal studies have shown that removing senescent cells extends remaining life by more than 33%.
“Since telomere shortening is considered the ‘Holy Grail’ of the biology of ageing, many pharmacological and environmental interventions are being extensively explored in the hopes of enabling telomere elongation,” said one of the scientists involved in the research, Professor Shai Efrati, Director of the Sagol Center at Shamir Medical Center.
“The significant improvement of telomere length shown during and after these unique protocols provides the scientific community with a new foundation of understanding that ageing can indeed be targeted and reversed at the basic cellular-biological level.”
Scientists believe ageing itself is responsible for diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, arthritis, cancer, heart disease and diabetes.
It is known that obesity, smoking, lack of physical activity, vitamin deficiency and inflammation can speed up the shortening of telomeres, demonstrating that they have a major impact on the length of a life.
The 35 participants did not undergo any lifestyle, diet or medication adjustments. Each patient was placed in a hyperbaric chamber for 90 minutes for five days a week over three months while breathing 100% oxygen through a mask.
The pressurized chamber allows more oxygen to be dissolved into the tissues and mimics a state of hypoxia, or oxygen shortage, which is known to have regenerating effects.
Previous trials have shown that eating a healthy diet can preserve telomere length, while high-intensity training for six months has been proven to lengthen telomeres by up to 5%.
The Israeli team has also previously demonstrated that the pressurised oxygen therapy can improve cognitive decline.
“Until now, interventions such as lifestyle modifications and intense exercise were shown to have some inhibition effect on the expected telomere length shortening,” said Dr Amir Hadanny, Chief Medical Research Officer of the Sagol Center for Hyperbaric Medicine and Research.
“However, what is remarkable to note in our study is that, in just three months of therapy, we were able to achieve such significant telomere elongation – at rates far beyond any of the current available interventions or lifestyle modifications.”
About The Scientists Professor Shai Efrati (pictured above) is an Israeli physician. He is also an associate professor at the Sagol School of Neuroscience at Tel Aviv University.
Moreover, his title includes director of the The Sagol Center for Hyperbaric Medicine and Research at Shamir Medical Center at the Shamir Medical Center in Israel. Professor Efrati is also medical advisor and serves as Chair of Aviv Scientific’s Medical Advisory Board.
Amir Hadanny, MD is a senior physician, certified neurosurgeon and a hyperbaric physician and Chief Medical Research Officer at the Sagol Center for Hyperbaric Medicine and Research and Shamir Medical Center.
For the past decade, Dr. Hadanny has worked alongside Professor Shai Efrati on novel research focused on neuro-rehabilitation, neuro-plasticity and physiology. He has published more than 25 research papers focused on the effects of HBOT.
“With this pioneering study, we have opened a door for further research on the prolonged cellular impact of the therapy to reverse the ageing process. After dedicating our research to exploring its impact on the areas of brain functionality and age-related cognitive decline, we have now uncovered, for the first time in humans, biological effects at the cellular level in healthy ageing adults.”
The researchers pointed out that the study has several limitations and strengths to consider. First, the limited sample size has to be taken into account. Second, the lack of a control group.
“However, the study suggests impressive results on telomeres and senescent cell clearance, which weren’t observed in other interventions,” said the research paper.
Hope for your ageing brain and failing memory! @TelAvivUniversity & The Sagol Center for Hyperbaric Medicine & Research at Shamir Medical Center announce ground breaking anti ageing research
Full Interview: https://t.co/6A4Lb5wSdh @giselewaymes @neurology_live @JanineBester pic.twitter.com/LdD45drjSY— Bronwyn Nielsen (@bronwynnielsen) November 18, 2020
For The First-Time A Human Study Shows The Reversal In Biology Of Aging, With Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
TEL AVIV – November 18, 2020: In a scientifically verified approach, signalling an important breakthrough in the study of aging, Tel Aviv University and The Sagol Center for Hyperbaric Medicine and Research at Shamir Medical Center announced today that, for the first time in humans, two key biological hallmarks of aging, telomere length shortening, and accumulation of senescent cells, can be reversed.
The prospective clinical trial, published in peer-reviewed Journal Aging, utilizes Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy protocols to demonstrate cellular level improvement in healthy aging adults.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Targets Aging As A Reversible Disease
The prospective clinical trial is part of a comprehensive aging research program taking place in Israel. It was conducted by Prof. Shai Efrati, MD, from the Faculty of Medicine and Sagol School of Neuroscience at Tel Aviv University, and Amir Hadanny, MD, Chief Medical Research Officer of The Sagol Center for Hyperbaric Medicine and Research and co-author of the study.
Using a specific protocol of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), telomere length was significantly increased and senescent cells were reduced in a population of healthy aging subjects.
The study was published in the peer-reviewed journal Aging. Titled: Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Increases Telomere Length and Decreases Immunosenescence in Isolated Blood Cells: A Prospective Trial.
A Significant Breakthrough In The Study Of Aging
The biological deterioration of aging is cited as a major risk factor for cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease. At the cellular level, two key hallmarks of the aging process are:
- The shortening of telomere length of approximately 20-40 bases per year, which is associated with a variety of serious life-threatening illnesses; and
- The accumulation of senescent cells, the so-called “old malfunctioning cells,” inhibit cell proliferation. The accumulation of senescence contributes to many age-associated conditions and illnesses, while the elimination of those cells can reverse them, as shown in previous animal studies.
The First Study To Evaluate Telomere Length And Senescence
This is the first study to evaluate whether hyperbaric oxygen therapy can affect telomere length and senescence using a specific HBOT protocol. The trial included 35 healthy independent adults aged 64 and older. They did not undergo any lifestyle, diet, or medication adjustments.
How Was The Study Conducted?
Each patient received 60 daily hyperbaric oxygen therapy sessions over the course of 90 days. Whole blood samples were collected prior to treatment, at the 30th and 60th session, and one to two weeks following the last HBOT session, to assess peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PMBCs) telomere length and senescence.
The Holy Grail Of The Biology Of Aging
“After dedicating our HBOT research to exploring its impact on the areas of brain functionality and age-related cognitive decline, we have now uncovered for the first time in humans hyperbaric oxygen therapy’s biological effects at the cellular level in healthy aging adults,” said Prof. Shai Efrati.
“Since telomere shortening is considered the ‘Holy Grail’ of the biology of aging, many pharmacological and environmental interventions are being extensively explored in the hopes of enabling telomere elongation.”
Significant Improvement Of Telomere Length
“The significant improvement of telomere length shown during and after these unique hyperbaric oxygen therapy protocols provides the scientific community with a new foundation of understanding that aging can, indeed, be targeted and reversed at the basic cellular-biological level.”
Improvement In Just Three Months
Results found that the telomere length of T helper, T cytotoxic, natural killer, and B cells increased significantly. They rose by over 20 percent, following HBOT. The most significant change was in B cells, which increased during the 30th session, 60th session, and post HBOT by:
- 25.68%±40.42 (p=0.007)
- 29.39%±23.39 (p=0.0001)
- 37.63%±52.73 (p=0.007)
In addition, there was a significant decrease in the number of senescent T helpers by -37.30%±33.04 post-HBOT (P<0.0001). T-cytotoxic senescent cell percentages decreased significantly by -10.96%±12.59 (p=0.0004) post-HBOT.
“Until now, interventions such as lifestyle modifications and intense exercise were shown to have some inhibition effect on the expected telomere length shortening,” explained Dr. Hadanny.
Reverse The Aging Process!
“However, what is remarkable to note in our study, is that in just three months of hyperbaric oxygen therapy we were able to achieve such significant telomere elongation – at rates far beyond any of the current available interventions or lifestyle modifications.
With this pioneering study, we have opened a door for further research on the prolonged cellular impact of HBOT to reverse the aging process.”
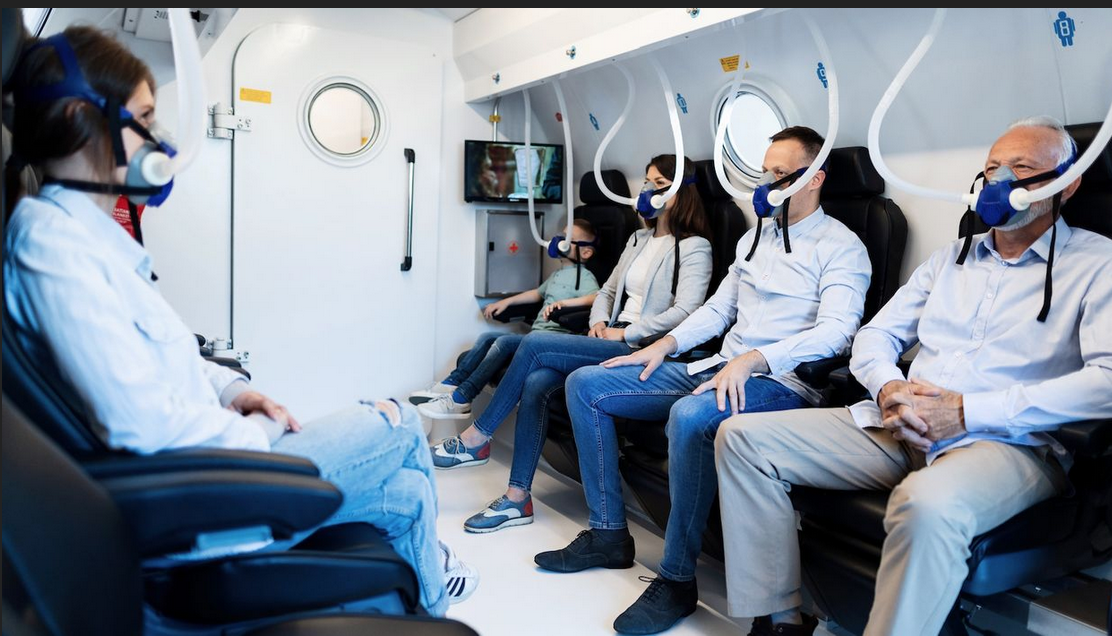
What Is A Hyperbaric Oxygen Chamber?
Hyperbaric oxygen has been used to treat several illnesses and injuries for which the FDA has approved. According to Johns Hopkins, hyperbaric oxygen therapy was first used in the U.S. in the early 20th century. “This was when Orville Cunningham used pure oxygen to successfully treat someone dying from the flu.
He developed a hyperbaric oxygen chamber but dismantled it after his use of therapy for other conditions failed. The therapy was tried again in the 1940s when the U.S. Navy used hyperbaric oxygen to treat deep-sea divers who had decompression sickness. By the 1960s, the therapy was also used to combat carbon monoxide poisoning.
Today, it’s still used to treat sick scuba divers and people suffering from carbon monoxide poisoning, including firefighters and miners. It has also been approved for more than a dozen conditions ranging from wound care, burns to bone disease:”
How Does It Work?
Firstly, there is a notable difference between portable hyperbaric oxygen therapy chambers or pods you can buy on the internet and even those you may use at walk-in health centres.
This is not to be confused with medically designed, approved hyperbaric oxygen therapy suites referred to in this scientific study.
According to the Mayo Clinic, hyperbaric oxygen therapy is generally a safe procedure. Complications are rare. But this treatment does carry some risk.
Nobel Prize For Medicine
Research into the revitalizing powers of oxygen has been in the spotlight recently. In October 2019, the Nobel Prize for Medicine was awarded to three researchers for their discovery of how living cells sense and react to changes in oxygen levels.
Maximize Rejuvenation
Our body senses fluctuations in oxygen and that rejuvenation processes can actually be triggered by these oxygen fluctuations.
This is one of the main principles behind the hyperbaric oxygen therapy medical protocol. The treatment involves the inhalation of 100% pure oxygen while sitting in a large HBOT suite.
The chamber is pressurized with air to above atmospheric levels. During HBOT, oxygen levels in the body’s tissues rise 10-15 times over that of normal conditions.
First, it increases the oxygen levels in the body’s tissues. It then fluctuates the level of oxygen in the body to enhance the body’s natural processes of rejuvenation. By controlling and combining these two processes, the medical team can maximize the rejuvenation potential of a person’s body and brain.
How Long Is The Treatment?
The treatment begins with three days of intensive assessments, identifying a person’s baseline cognitive and physical performance. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy sessions will take approximately two hours per day, five days a week, for 12 weeks.
Two to three times a week, at a designated clinic and increased to 2.5 hours to allow the person to participate in additional on-site training if needed.
How Long Do The Results Last?
The longevity of results varies from one individual to the next. They also depend on the person’s individual biology and lifestyle – mainly nutrition and physical activity.
In terms of the study, in just three months of HBOT, the scientists were able to achieve a significant telomere elongation. This is at a rate far beyond any of the currently available interventions or lifestyle modifications.
Can Pure Oxygen Reverse Effects Of Ageing? People Placed In Pressurised Chambers Gain Significant Benefits From Breathing Clean Air, Research Shows
* Breathing Pure Oxygen May Help To Reverse The Ageing Process, Scientists Claim
* Found Those Put In Pressurised Oxygen Chambers Gained Significant Benefits
* Sessions Lasted 90 Minutes Each And Took Place For Five Days A Week Over Three Months
Breathing pure oxygen may help to reverse the ageing process, the scientists behind a breakthrough study claim.
They found that subjects put in pressurised oxygen chambers gained significant benefits.
Firstly, it enabled telomeres – the protective caps on chromosomes – to regrow by more than 20 per cent.
Telomeres naturally become shorter with age, leading to illnesses including cancer, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
But in the experiment they grew back to the length of people 25 years younger.
The study also found that the number of senescent cells – which prevent regeneration as they build up in the body – was cut by up to 37 per cent. Removing the so-called zombie cells can extend life.
Professor Shai Efrati of the Faculty of Medicine at Tel Aviv University said: ‘Since telomere shortening is considered the ‘Holy Grail’ of the biology of ageing, many pharmacological and environmental interventions are being extensively explored in the hopes of enabling telomere elongation.
‘The significant improvement of telomere length shown during and after these unique protocols provides the scientific community with a new foundation of understanding that ageing can indeed be targeted and reversed at the basic cellular-biological level.’
In the study, published in the journal Ageing, 35 healthy adults aged 64 and older breathed in 100 per cent oxygen through a mask whilst sitting in pressurised chambers.
The sessions lasted 90 minutes each and took place for five days a week over three months.
The pressurised chamber mimics a state of ‘hypoxia’, or oxygen shortage, enabling tissues to dissolve more oxygen which has well-known regenerative effects.
Previous trials revealed that healthy eating and high-intensity exercise can also preserve telomere length – but this experiment far outdid natural interventions, the researches explained.
Study researcher Dr Amir Hadanny, of Tel Aviv’s Sagol Center for Hyperbaric Medicine and Research, said: ‘Until now, interventions such as lifestyle modifications and intense exercise were shown to have some inhibition effect on the expected telomere length shortening.
‘However, what is remarkable to note in our study is that, in just three months of therapy, we were able to achieve such significant telomere elongation – at rates far beyond any of the current available interventions or lifestyle modifications.’
Inquiry into the evolution of aging aims to explain why almost all living things weaken and die with age. A Users Guide To Immortality
There is not yet agreement in the scientific community on a single answer. The evolutionary origin of senescence remains a fundamental unsolved problem in biology.
Historically, aging was first likened to “wear and tear”: living bodies get weaker just as with use a knife’s edge becomes dulled or with exposure to air and moisture iron objects rust.
Prospects For Extending Healthy Life – A Lot
But this idea was discredited in the 19th century when the second law of thermodynamics was formalized.
Entropy (disorder) must increase inevitably within a closed system , but living beings are not closed systems . It is a defining feature of life that it takes in free energy from the environment and unloads its entropy as waste.
Living systems can even build themselves up from seed, and routinely repair themselves. There is no thermodynamic necessity for senescence. In addition, generic damage or “wear and tear” theories could not explain why biologically similar organisms (e.g. mammals ) exhibited such dramatically different life spans.
Furthermore, this initial theory failed to explain why most organisms maintain themselves so efficiently until adulthood and then, after reproductive maturity, begin to succumb to age-related damage.
THE IMMORTALISTS – A Short Film By Jason Silva
Aging has been slowed and healthy lifespan prolonged in many disparate animal models (C. elegans, Drosophila, Ames dwarf mice, etc.). Thus, assuming there are common fundamental mechanisms, it should also be possible to slow aging in humans.
Greater knowledge about aging should bring better management of the debilitating pathologies associated with aging, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, type II diabetes, and Alzheimer’s.
Therapies targeted at the fundamental mechanisms of aging will be instrumental in counteracting these age-related pathologies.
Eliminating Cancer With Nanotechnology
Therefore, this blog is a call to action for greater funding and research into both the underlying mechanisms of aging and methods for its postponement. Such research may yield dividends far greater than equal efforts to combat the age-related diseases themselves.
Personalized Medicine Drugs Tailored To Your Genetic Makeup
Personalized Medicine: Using an individual’s own genetic information to guide better treatment and prevention of diseases–is one of the most talked-about areas in healthcare.
To understand how personalized medicine may play out in real life, consider a frequent traveler whose business takes him or her to Asia, South America or Africa.
In all of those places, mosquitoes spread dengue fever–a rapidly-growing, infectious tropical disease for which there is no vaccine.
People who contract dengue fever can have a wide range of reactions. A fortunate few develop no symptoms at all. Others experience a week of flu-like symptoms–high fever, vomiting, headaches, muscle pain or a measles-like rash.
However, a small number of people develop a life-threatening variety known as dengue hemorrhagic fever. Diagnosing and treating the disease quickly, especially the more severe variety, has always been challenging for doctors.
How does this relate to personalized medicine? Allan Brasier, director of the Institute for Translational Sciences at the University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB) , led a team that identified protein markers that may be able to predict a predisposition toward developing dengue fever and dengue hemorrhagic fever.
In the future, these markers could guide physicians to take earlier steps with those who show symptoms and are at high risk for the more serious strain of the disease. They could receive transfusions and other early intervention strategies that could save more lives.
This has been the goal of personalized medicine since the human genome was first sequenced in 1993. “Personalized medicine could eliminate the trial-and-error approach of giving every patient with the same disease the identical drugs or treatment ,” Brasier says.
“We can identify subgroups that have the same disease and can be targeted for different treatments based on their genetic information.” The goal is to avoid wasting time and money on potentially ineffective treatments, which expose many patients to harmful side effects.
Genomics and Disease
Clay Marsh, M.D., executive director of the Center for Personalized Health Care at The Ohio State University Medical Center , explains the leading uses for personalized medicine so far have been treatments for cancer and infectious diseases, along with better targeting of pharmaceuticals.
“Cancer is the most clinically applicable domain of genomics in medicine today. A cancer cell is clearly identifiable as the problematic cause of the disease and genetic profiling has identified key cellular pathways to target with specific drugs.
Similarly, infectious disease cells can also be genetically fingerprinted for a specific disease, and this is the next exciting application of genomics. Other diseases are proving to be more complex to fingerprint.”
Currently, there are an estimated 300 Phase II or higher oncology drugs that are being developed which have the potential for testing against a genetic biomarker . Right now, molecular testing is helping identify which patients with breast cancer and colon cancer are likely to benefit from different treatments.
For example, a gene expression test has been developed that can help determine which patients with breast cancer might benefit from chemotherapy. Joseph Sparano, M.D., associate chairman of the department of oncology at Montefiore Einstein Center for Cancer Care in New York , says the test measures the activity level of a panel of genes within the tumor sample, and the result correlates with the likelihood of having breast cancer recurrence.
Because of this information, doctors can identify a subset of patients who are likely to be cured with surgery and hormonal therapy alone, sparing them the need to undergo chemotherapy after surgery.
Clinical trials are underway to help guide treatment of the 25 to 50 percent of patients who fall into the “gray” area–the intermediate risk category–for which the best course of action is unclear.

Personalized Prescriptions
, the science of how a person’s genetics affects how they respond to certain medications, is another key area of personalized medicine. Variations in DNA affect how an individual’s body absorbs, metabolizes and uses drugs.
Michael Christman, Ph.D., president and chief executive officer of the Coriell Institute for Medical Research , a nonprofit biomedical research institution in Camden, N.J., points to clopidogrel , a medication that is prescribed after someone has a heart attack or stent placement.
“Up to 30 percent of people prescribed the medication do not activate the drug, and may as well take sugar pills,” he says. “However, there is an alternative FDA-approved drug, and if genetic testing were performed for the patient prior to dosing, the best drug could be selected first .”
This is hardly an isolated example. Personalized medicine has the potential to assist the large number of people who are prescribed medication that provides them no benefit because of their individual genetic response.
“Right now, we know that one-third of the people who receive a drug get a positive response, one-third get no response, and one-third get a toxic response,” says Jonathan S. Dordick, Ph.D., director of the Center for Biotechnology & Interdisciplinary Studies at the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute . “By tailoring drugs to the physiologic of the person, we can change the number of people who get a beneficial response from one-third to two-thirds. And we can reduce the negative reaction from one-third to one-sixth.”
That means fewer trial-and-error prescriptions and a steep drop in the number of adverse drug reactions, which cause more than 770,000 injuries and deaths a year in the U.S .
Faster Time To Market
Genetic information could also provide benefits in how new drugs are developed. Dordick points out that pharmaceutical companies now focus on developing drugs that have a large enough potential to generate $1.5 billion to $2 billion in revenues. That’s primarily because the complex drug approval and clinical trial process is so costly.
The promise of personalized medicine is that instead of developing, say, one drug for asthma, a pharmaceutical company could develop five different versions of the drug designed for different populations based on their genetics.
However, one issue is that each of these five versions, under the current drug development framework, would need to undergo the expensive drug approval and testing process. That may not be cost effective since the testing costs would increase fivefold, but the amount of revenue the five drugs generate in total would not be five times that of a single version of the drug.
Dordick envisions new testing techniques that would make it more viable to develop a series of drugs for genetic subgroups of patients.
For one thing, he suggests eliminating the initial step of testing a drug’s efficacy on rats or dogs–the idea is that if human genetics are so dissimilar that not every drug will work with every human, there is no reason to spend time and money testing the drugs on biologically dissimilar creatures.
Instead, researchers could leverage new technologies that test the toxicity and effectiveness of new drug molecules using individual human cell cultures. In essence, at some point, a doctor could test how effectively a drug would work for you by testing your own cells.
If such tools were integrated into the drug approval process, Dordick says they could speed the process, reduce the costs, and weed out unsafe or ineffective drugs early in the process.
“If you are giving a drug to a specific set of the patient population, you can get very high quality candidates for testing and shave a tremendous number of years off the development,” he says. ” Because the limited number of patients can be more easily classified, you will be able to use hundreds of patients in the clinical trials rather than thousands of patients .”
Inventing The Rules
At the same time, medical practitioners say that safeguards need to be put in place for how to use the evolving information about genetics in treatment. The Coriell Institute uses a scientific advisory panel composed of physicians, scientists and ethicists called the Informed Cohort Oversight Board (ICOB) to help determine what genetic variants will be used in guiding treatment for different diseases.
“We generate and present risk information to the ICOB panel that independently judges its validity. We abide by the panel’s expert decisions, even when they disagree with our recommendations,” Christman says. For example, research done by the Institute identified a genetic risk variant for breast cancer.
The researchers thought the variant could be useful in determining which women should receive a mammogram at an early age. However, an oncologist on the advisory panel noted the increased radiation risk from the earlier mammograms outweighed the predictive value of the genetic information.
As all this suggests, there are many questions about how to best integrate genetic information into the treatment of patients. Personalized medicine has huge promise, but it also brings up issues such as healthcare, payer and physician incentives, medical record privacy, and the ethics of clinical trials that will need to be worked through.
“This has happened so quickly,” says Brenda Finucane, a certified genetic counselor and president of the National Society of Genetic Counselors (NSGC) . “We have the genetic technology before we have evidence-based models on how to use the technology.
This is very different than other developments in medicine, where you had time to think about it for a while and developed evidence-based medicine. We don’t have time, so we are developing practice guidelines on the fly. Patients and healthcare providers will all be learning together as this gets rolled out.”
As the mechanisms of aging are increasingly understood, increasingly effective interventions can be developed that will help prolong the healthy and productive lifespans of a great many people .
Transending Human Capabilities
Transhumanism is an international intellectual and cultural movement that affirms the possibility and desirability of fundamentally transforming the human condition by developing and making widely available technologies to eliminate aging and to greatly enhance human intellectual, physical, and psychological capacities. Transhumanist thinkers study the potential benefits and dangers of emerging technologies that could overcome fundamental human limitations, as well as study the ethical matters involved in developing and using such technologies. They predict that human beings may eventually be able to transform themselves into beings with such greatly expanded abilities as to merit the label “posthuman”.
Bone Marrow Stem Cells
You have within you a powerful set of tools to repair your body and keep you healthy. The future of medicine is NOT better drugs but better use and application of your body’s own stem cells . As of now stem cell -rich tissue can be extracted from your hip with virtually no discomfort and used to help restore your body.
This opens up an exciting new horizon in terms of preventing and treating disease and tackling the symptoms of aging – if not aging itself. Already, patients are returning to Dr. Steenblock for additional bone marrow treatments because they are seeing that their gray or white hair is turning back to its original color. Their skin not infrequently looks younger too and they report having more energy and less arthritic aches and pains!
In regard to its anti-aging effects, the bone marrow contains primitive progenitor cells that are associated with the early development of the fetus. These primitive cells reside dormant deep inside your bones and sport a genetic profile from your early development.
When these primitive cells are released into your system, there can be a revitalization of your body that physiologically “sets the clock back” in-a-way. Several patients have reported that the bone marrow transplants have also improved their sexual performance. This side effect is thought to be the result of stem and progenitor cells repairing sex organs as well as other tissues.
What does this mean for you? Your bone marrow stem cells have the potential to repair damaged tissues and organs. Whether you want an ” anti-aging “ treatment or you need the procedure to repair damage in your joints, liver, kidneys, heart or brain, a bone marrow transplant is an efficient and sure way to flood your body with stem cells.
Simple Test s Determine How Long You’ll Live
The Power of Knowing
Telomere length is one of the best biomarkers of overall health status. It is a major “integrator” of current and lifelong factors that impact health, including genetics, diet, fitness, toxins, and chronic stress. Knowing your telomere length (and monitoring changes over time) can provide valuable information on your disease risk – or even the rate at which you are aging. With this information, you have the knowledge to change the quality of your life and health status at a cellular level.
The Power of Change
Telomeres are the only “changeable” part of the genome, and positive lifestyle choices can increase telomere length and promote individual wellness. Your Cells are Your Guide to Personalized Solutions for Optimal Health Monitoring your telomere length over time can provide insights about potential disease risk and your rate of physiological aging. This knowledge can help to inform your lifestyle and, eventually, as research reveals more specific applications, it may also help inform therapeutic or prophylactic drug choices and decisions.
“Knowing whether our telomeres are a normal length or not for a given chronological age will give us an indication of our health status and of our physiological ‘age’ even before diseases appear,” says Maria A. Blasco , who heads the Telomeres and Telomerase Group at the Spanish National Cancer Research Center and who co-founded the company Life Length .
Telomere research pioneer Calvin B. Harley, who co-founded Telome Health last spring with Nobel laureate Elizabeth H. Blackburn , considers telomere length ” probably the best single measure of our integrated genetics, previous lifestyle and environmental exposures .”
Soon the companies will offer telomere-measurement tests to research centers and companies studying the role of telomeres in aging and disease; the general public may have access soon after through doctors and laboratories, perhaps even directly.
When Human Brain Cells Meet Silicon Chips
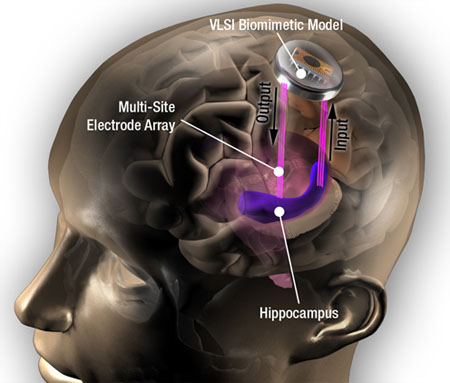
Direct interfaces between small networks of nerve cells and synthetic devices promise to advance our understanding of neuronal function and may yield a new generation of hybrid devices that exploit the computational capacities of biological neural networks. There are several research teams in the U.S. and Europe that are currently working on so-called neural-silicon hybrid chips.
One of the most celebrated researchers in the field is Ted Berger at the Center for Neural Engineering at University of Southern California in Los Angeles . Berger is also a key player in the newly established National Science Foundation Engineering Research Center devoted to biomimetic microelectronics.
Berger has set his sights on building artificial neural cells, initially to act as a cortical prosthesis for individuals who have lost brain cells to neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s. But eventually, his lab’s efforts may usher in a new era in biologically inspired computing and information processing.
Berger’s strategy in building artificial neurons has been an empirical one. Rather than attempt to determine every aspect of how neurons communicate, he’s chosen to emulate their behavior, bombarding live neurons from rat hippocampus tissue with every conceivable type of electrical input, and observe what output emerges from the cell.
His team at USC then built a silicon microcircuit that behaves accordingly, at least in terms of spatio-temporal patterns of electrical inputs and outputs. The USC team has built circuits that model 100 neurons; their goal is to construct a 10,000-neuron chip model for implantation in primate hippocampus.
The Max Planck Institute in Germany is another center of research on neural-silicon hybrids. Recently, RA Kaul and P. Fromhertz from the Institute and NI Syed from the University of Calgary reported in Physical Review Letters on direct interfacing between a silicon chip and a biological excitatory synapse.
The team constructed a silicon-neuron hybrid circuit by culturing a presynaptic nerve cell atop a capacitor and transistor gate and a postsynaptic nerve cell atop a second transistor gate.
They applied a voltage to the capacitor, which excited the presynaptic neuron, and this activity was recorded with the first transistor. When the presynaptic neuron fired, it generated excitation of the postsynaptic neuron, presumably via an excitatory synapses, and the activity in the postsynaptic neuron was recorded with the second transistor. Further, short trains of activity in the presynaptic neuron appeared to increase the strength of the excitatory synapse between the cells, creating a memory trace within the circuit.
These results demonstrate the ability to use integrated capacitors and transistors to stimulate and record from cultured neurons. The neuron-silicon hybrid provides a tool to study formation and plasticity within small neural circuits and may lead to novel computational devices.
Fasting 101: Rebooting The Body’s Hard Drive: Rejuvenating, Life-Extending And Removes Deadly Toxins.
When Diet Is Wrong Medicine Is of No Use.
When Diet Is Correct Medicine Is of No Need.
~Ayurvedic Proverb
Updated: 2-15-2022
Centenarian-Sourced Probiotic Mixed With Dietary Fiber Has Anti-Aging Effects
A probiotic strain isolated from centenarians’ feces combined with dietary fiber showed beneficial effects on brain and gut function and has potential as an aging treatment for the elderly.
Highlights
* A probiotic isolated from centenarians called LTL1361 mixed with dietary fiber alleviates age-related cognitive impairment and protects the brain of healthy aging mice.
* This probiotic and dietary fiber combination also improves gut function and reduces inflammation in the blood and colon.
* These findings suggest the LTL1361 and dietary fiber mixture as a novel and promising anti-aging agent in humans.
Accumulating evidence indicates that gut microbiota regulates host health. This microorganism population can be manipulated in multiple ways: with probiotics to change the variety and with dietary nutrients or fiber to supply specific compounds.
While studies have focused on the anti-aging effects within a particular disease, the evidence is limited for the anti-aging effects of centenarian-sourced probiotics combined with a dietary fiber complex.
Researchers from Guangxi University in China reveal the anti-aging effects of an isolated probiotic strain from healthy centenarians’ feces mixed with dietary fiber.
With three months of treatment, this combination improved learning and memory ability, antioxidant capacity, and inflammation markers in aged mice.
Published in the journal Nutrients, the researchers suggest that probiotics and dietary fiber combination might be used as a novel and promising anti-aging synbiotic agent in humans.
Fighting Aging With Feces-Sourced Probiotics And Fiber
As aging is inevitable and its relative negative symptoms are complicated, we tend to pursue anti-aging treatments, ranging from diets to drugs. Accumulating evidence has indicated that prebiotics and probiotics could affect our health by regulating our gut microbiota.
Prebiotics — a form of dietary fiber that feeds the “friendly” bacteria in your gut — are resistant to digestion and absorption during passage through the stomach and small intestine but can be fermented in the large intestine by gut bacteria.
This dietary fiber can influence our gut bacteria to produce beneficial metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). But data indicate that daily dietary fiber intake for the elderly is roughly 40% below the recommended adequate intake.
For example, concentrations of SCFAs, which may promote weight loss and provide various health benefits, are less optimal in the elderly.
Live microorganisms called probiotics — like the ones advertised in cultured dairy products (e.g., yogurt and kefir) — administered in adequate amounts exert health benefits to the host.
Probiotic strains derived from the elderly exhibit excellent antioxidant, cholesterol-lowering, and immune-regulating activities.
Lactobacillus is the largest probiotic group with a high possibility of developing functional food. However, individual bacterial strains always exhibit unique bioactivities that require experimental confirmation.
Several Lactobacillus strains have been reported to have anti-aging effects due to their radical-scavenging activity and oxidation stress-attenuating ability.
Centenarian-Sourced Probiotic And Dietary Fiber Improve Aging In Mice
Previously, the Guangxi University research team isolated a strain of Lactobacillus — which they named LTL1361 — from the feces of healthy centenarians living in Bama, China, and demonstrated its potential probiotic properties in preliminary research in cultured cells.
In this study, Ren and colleagues examined the anti-aging effects of the LTL1361 strain and dietary fiber on learning and memory ability, antioxidant capacity, inflammation markers, and SCFAs in natural aging mice.
Using the Morris water maze test of spatial memory, the Guangxi University researchers evaluated the effects of dietary fiber and LTL1361 on cognitive abilities in aged mice. Researchers used the Morris water maze to study spatial memory and learning.
In this test, animals are repeatedly placed in an opaque pool of water surrounded by environmental cues, where they are tracked as they learn to find a hidden escape platform.
The researchers observed a reduction in the time it took aged mice treated with dietary fiber or LTL136 to find the platform. The results revealed that the combination of dietary fiber and centenarian-sourced LTL1361 significantly improved learning and memory ability.
In addition to improving learning and memory, Ren and colleagues showed that the combination of dietary fiber and Lactobacillus LTL1361 protected intestinal wall function and areas of the brain associated with cognition (pyramidal neurons) and learning/memory (hippocampus).
Furthermore, LTL1361 and dietary fiber decreased oxidative stress and inflammation and increased the availability of SCFAs in the small intestine.
Can Probiotics And Fiber Improve Human Aging?
The combination of dietary fiber and Lactobacillus LTL1361, which is a synbiotic (mixture of probiotics and prebiotics) seems like a promising treatment for cognitive decline in the elderly.
Nevertheless, further studies are required to clarify the biological connection between our gut, the microorganisms living within our gut, and how they affect our brain during aging.
Most of the latest clinical research has focused on applying commercial probiotics (one strain or a cocktail) to healthy older people.
The results indicate that probiotic consumption may positively impact by increasing the levels of specific beneficial gut microbe populations or modifying subpopulations of Lactobacillus.
These studies show that probiotics can enhance the immune response and improve bowel movements, among other beneficial effects.
Other studies have shown that the health benefits of probiotics are related to their ability to revert age-related increases of opportunistic pathogens, such as Clostridium difficile, which are involved in antibiotic-associated diarrhea that impact nutrition and inflammatory status.
In the elderly, C. difficile-associated diarrhea was linked to a reduction in the number of Bifidobacteria. For this reason, therapies based on the use of probiotics to correct the microbiota imbalance seem promising.
However, current guidelines do not recommend their administration. Notwithstanding the promising results, other studies reported controversial ones, most of them having no significant effects.
Source:
Ren M, Li H, Fu Z, Li Q. Centenarian-Sourced Lactobacillus casei Combined with Dietary Fiber Complex Ameliorates Brain and Gut Function in Aged Mice. Nutrients. 2022 Jan 13;14(2):324. doi: 10.3390/nu14020324. PMID: 35057509; PMCID: PMC8781173.
Updated: 4-10-2022
This Is What The World’s Oldest Person Ate Every Day
A recent study by UK-based CBD company Eden’s Gate sought to uncover the secrets to living a long life by studying some of the world’s oldest people (via Eat This, Not That!).
To get at the core of what gives individuals health and longevity, researchers examined the lifestyles of six people who lived to be older than 100.
Their results indicated that four main factors determine longevity — movement, socioeconomic status, stress levels, and diet. Of those categories, diet may be the one that people have the most control over.
There are plenty of foods that science says will help you live longer. For example, nuts, berries, and fish are known to provide essential nutrients that contribute to a long life by boosting immunity and improving heart health.
The Eden’s Gate study took a direct approach to gathering information by examining the diet of the oldest person from their sample of research subjects. At 122 years old, Jeanne Louise Calment is the only person to ever live past 120.
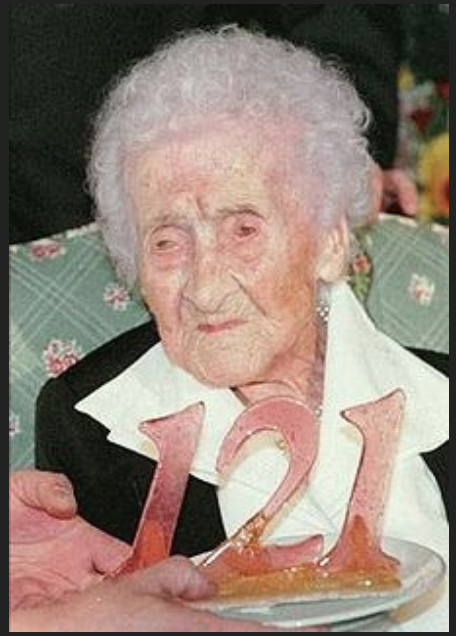

The Three Key Ingredients Of A Long Life
As Eat This, Not That! reports, CBD company Eden’s Gate studied the diet of the only person to ever live to 122 years old. In doing so, they identified three foods that may help you live longer.
Jeanne Louise Calment, who died in 1977, reportedly said olive oil was one of her secrets to a long healthy life.
According to Healthline, olive oil is rich in healthy fats, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory properties. It also may protect against heart disease and can decrease one’s chances of having a stroke.
Another key element in Calment’s diet was red wine, which the Mayo Clinic reports is heart healthy and flush with antioxidants. Experts recommend only consuming red wine in moderation, however.
Finally, chocolate-lovers can rejoice in the fact that their favorite sweet treat can add years to your life, according to both Calment and Hopkins Medicine. Like red wine, chocolate has heart-healthy qualities and can boost immunity.
It can also help your athletic performance by boosting brain function and supporting circulation in the blood. So, pour a glass of wine, drizzle some olive oil on your food, and follow it up with some chocolate for dessert. It’s all in the name of longevity.
Related Articles:
The Complete Guide To The Science Of Circadian Rhythms (#GotBitcoin?)
Billionaire is Turning Heads With Novel Approach To Fighting Cancer (#GotBitcoin?)
Fighting Cancer By Releasing The Brakes On The Immune System (#GotBitcoin?)
Over-Diagnosis And Over-Treatment Of Cancer In America Reaches Crisis Levels (#GotBitcoin?)
Cancer Super-Survivors Use Their Own Bodies To Fight The Disease (#GotBitcoin?)
The Benefits of Grounding or Earthing For Improved Health
Microbiome Live News
@metagenomics









Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.